
Sia
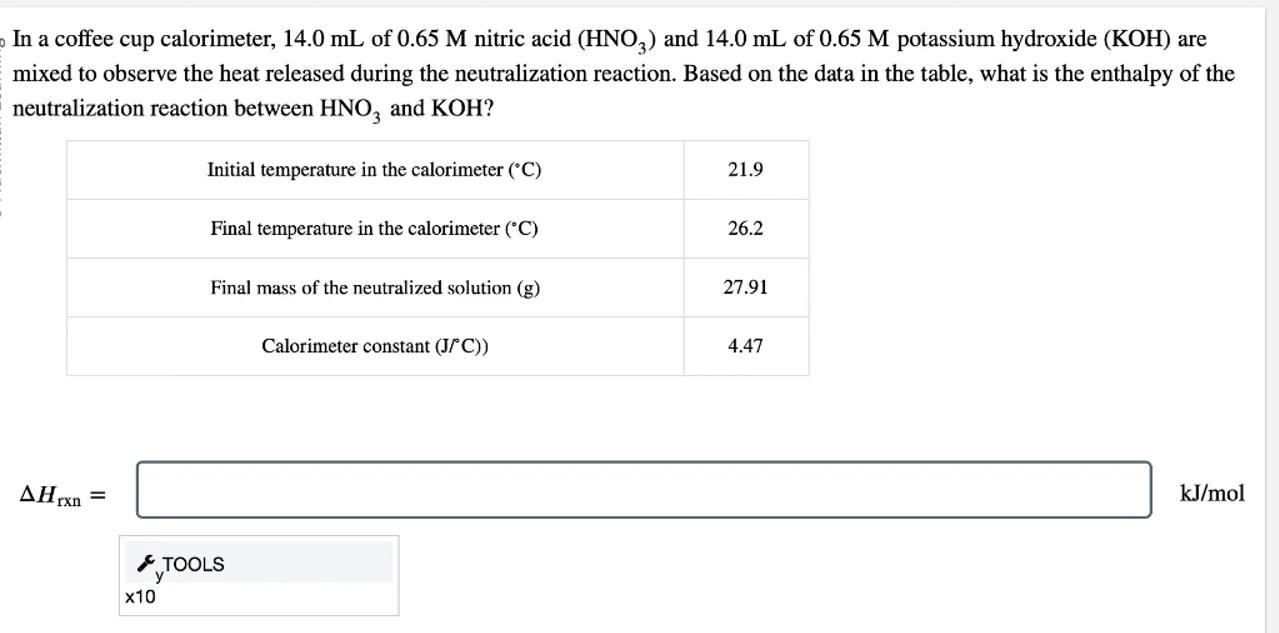
In a coffee cup calorimeter, of nitric acid and of potassium hydroxide are mixed to observe the heat released during the neutralization reaction. Based on the data in the table, what is the enthalpy of the neutralization reaction between and ?
\begin{tabular}{|c|c|}
\hline Initial temperature in the calorimeter & 21.9 \\
\hline Final temperature in the calorimeter & 26.2 \\
\hline Final mass of the neutralized solution & 27.91 \\
\hline Calorimeter constant & 4.47 \\
\hline
\end{tabular}

Answer from Sia
Posted almost 2 years ago
Solution
1
Identify the reaction: The reaction between nitric acid () and potassium hydroxide () is a neutralization reaction, which can be represented as:
2
Calculate the heat absorbed by the solution: The heat absorbed by the solution () can be calculated using the formula:
where is the mass of the solution, is the specific heat capacity of water (4.18 J/g°C), and is the change in temperature.
Given:
-
-
3
Calculate the heat absorbed by the calorimeter: The heat absorbed by the calorimeter () can be calculated using the formula:
where is the calorimeter constant.
Given:
-
-
4
Calculate the total heat released: The total heat released () is the sum of the heat absorbed by the solution and the calorimeter.
5
Calculate the moles of reactants: The moles of and can be calculated using the molarity and volume.
Given:
- Volume of and = 14.0 mL each
- Molarity of and = 0.65 M
6
Calculate the enthalpy change per mole: The enthalpy change of the reaction () can be calculated using the formula:
Given:
-
- Moles of reactants = 0.0091 mol
Answer
The enthalpy of the neutralization reaction between and is .
Key Concept
Enthalpy change of a reaction can be determined using calorimetry data and the formula .
Explanation
By calculating the heat absorbed by the solution and the calorimeter, and then dividing by the moles of reactants, we can determine the enthalpy change of the reaction.
Not the question you are looking for? Ask here!
Enter question by text
Enter question by image
Unlock Smarter Learning with AskSia Super!
Join Super, our all-in-one AI solution that can greatly improve your learning efficiency.
30% higher accuracy than GPT-4o
Entire learning journey support
The most student-friendly features
Study Other Question