
Sia

Question
Chemistry
Posted almost 2 years ago
Question 3 [30 marks]
The following chromatogram was obtained from the analysis of a commercial product that contained three main components and . The column used was a reversedphase analytical C18 column (dimensions ) and the mobile phase was a methanol / buffer mixture.
a. Rank the order of polarity of and with justification. [6 marks]
b. Calculate the resolution between and and use your result to decide if the two peaks are fully separated. [10 marks]
c. What would happen to the peak separation if the methanol concentration is (i) increased to or (ii) decreased to ? Justify your answers. [10 marks]
d. What would the effect on the resolution be when the flow rate is increased? I4 marks]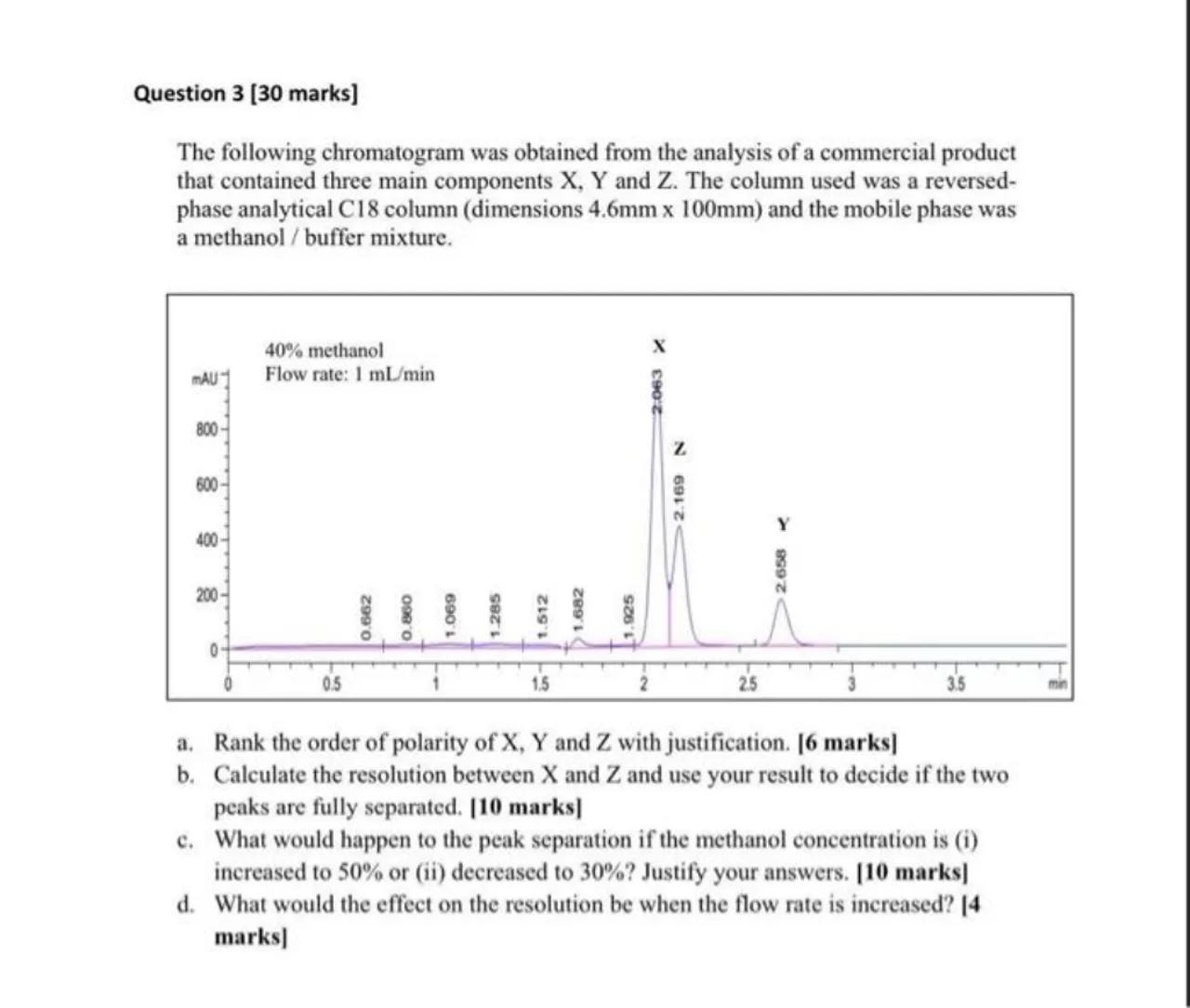

Answer from Sia
Posted almost 2 years ago
Solution
1
Understand chromatography principles: In reversed-phase chromatography, the stationary phase is nonpolar, while the mobile phase is polar. Substances with higher polarity elute faster because they have less interaction with the nonpolar stationary phase
2
Analyze retention times: Given the retention times of , , and as 2.063 min, 2.608 min, and 2.189 min respectively, we can infer their relative polarities
3
Rank polarities: Since has the longest retention time, it is the least polar. elutes before , making more polar than . Therefore, the order of polarity from most to least is
a Answer
The order of polarity from most to least is .
Key Concept
Polarity affects retention time in reversed-phase chromatography.
Explanation
More polar substances elute faster on a nonpolar stationary phase, leading to shorter retention times.
Solution
1
Understand resolution calculation: Resolution in chromatography is calculated using the formula , where and are the retention times of the two peaks and and are the base widths of the two peaks
2
Estimate peak widths: Since the chromatogram is not provided, we cannot measure the exact base widths of the peaks. For the purpose of this exercise, we will assume that the peak widths are similar and use the retention times to estimate resolution
3
Calculate resolution: Using the retention times provided, , where is the average base width of the peaks. Without exact peak widths, we cannot calculate a numerical value for resolution
4
Interpret resolution: A resolution of 1.5 or greater generally indicates that two peaks are fully separated. Without the exact peak widths, we cannot conclude if and are fully separated
b Answer
Without the peak widths, we cannot calculate the resolution or decide if and are fully separated.
Key Concept
Resolution is used to determine the separation of peaks in chromatography.
Explanation
A resolution of 1.5 or greater is needed for two peaks to be considered fully separated.
Solution
1
Understand the effect of methanol concentration: Methanol is the polar component of the mobile phase. Changing its concentration will affect the elution of analytes
2
Increased methanol concentration: Increasing the methanol concentration to 50% would make the mobile phase more polar, causing less polar components to elute faster and potentially reducing peak separation
3
Decreased methanol concentration: Decreasing the methanol concentration to 30% would make the mobile phase less polar, causing more polar components to elute slower and potentially increasing peak separation
c Answer
(i) Increasing methanol concentration to 50% may reduce peak separation. (ii) Decreasing methanol concentration to 30% may increase peak separation.
Key Concept
Methanol concentration affects the polarity of the mobile phase and the elution of analytes.
Explanation
More polar mobile phases can decrease the separation of less polar analytes, while less polar mobile phases can increase their separation.
Solution
1
Understand the effect of flow rate on resolution: The flow rate of the mobile phase can impact the resolution of peaks in chromatography
2
Increased flow rate: Increasing the flow rate can lead to a decrease in resolution because it may not allow sufficient time for the analytes to separate effectively on the column
d Answer
Increasing the flow rate may decrease the resolution of peaks.
Key Concept
Flow rate impacts the time analytes interact with the stationary phase.
Explanation
Faster flow rates can reduce the interaction time, leading to poorer separation and lower resolution.
Not the question you are looking for? Ask here!
Enter question by text
Enter question by image
Unlock Smarter Learning with AskSia Super!
Join Super, our all-in-one AI solution that can greatly improve your learning efficiency.
30% higher accuracy than GPT-4o
Entire learning journey support
The most student-friendly features
Study Other Question