
Sia
a. Compound is the major product formed in the reaction of compounds and as shown below:
(i) Draw the chemical structure of product .
[3 marks]
(ii) Draw and discuss in detail the reaction mechanism for the formation of compound from starting materials and . What is the name of this type of reaction?
[15 marks]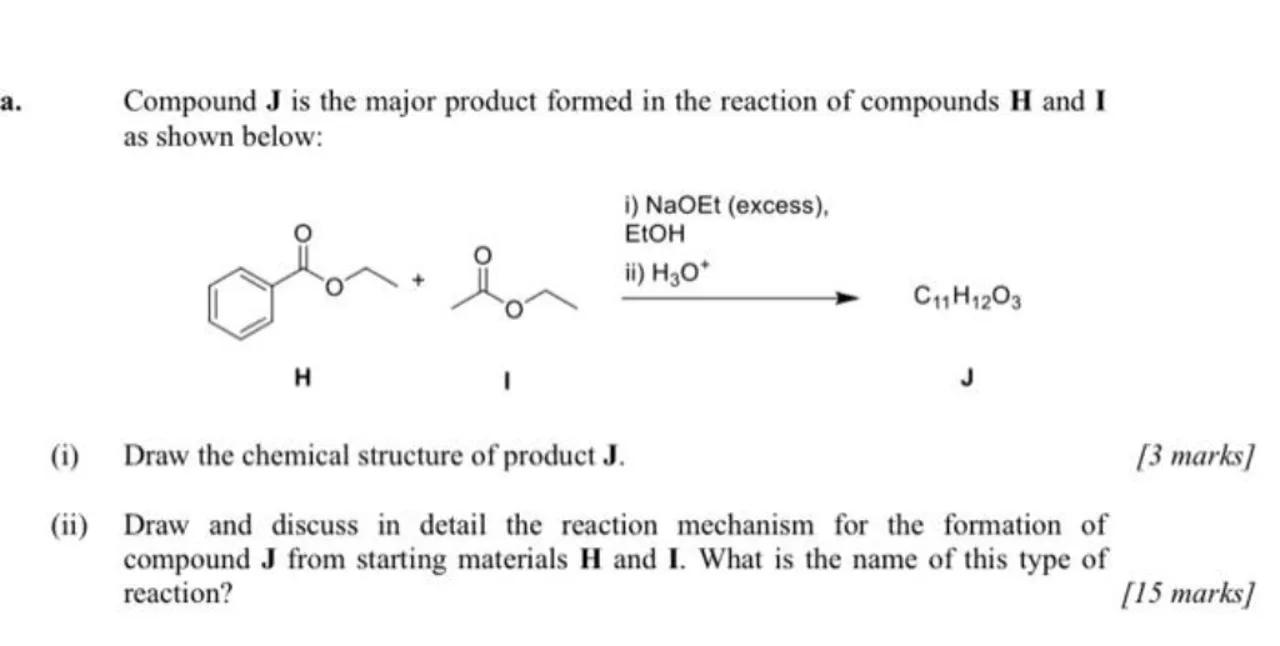

Answer from Sia
Posted almost 2 years ago
Solution
1
Predict the product J: Given the reaction conditions and the molecular formula of the product , we can deduce that a Claisen condensation followed by an acid-catalyzed cyclization occurs
2
Draw the structure of J: Based on the Claisen condensation, the ethyl group from compound I will form a bond with the carbonyl carbon of compound H. After cyclization, the final product will have a six-membered ring attached to the benzene ring, forming a 3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-one structure
3
Reaction mechanism: The mechanism involves the deprotonation of compound I by NaOEt to form an enolate, which then attacks the carbonyl carbon of compound H. After the condensation step, acid-catalyzed cyclization leads to the formation of the chromenone ring system
4
Name of the reaction: This reaction is a combination of a Claisen condensation and an acid-catalyzed cyclization, which can be referred to as a Claisen-Schmidt condensation followed by a cyclization to form the chromenone system
1 Answer
The chemical structure of product is a 3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-one derivative with the molecular formula .
2 Answer
The reaction mechanism involves a Claisen condensation followed by an acid-catalyzed cyclization to form the chromenone ring system. The reaction is a combination of Claisen and Schmidt condensation followed by cyclization.
Key Concept
Claisen condensation and cyclization
Explanation
The reaction between compounds H and I under basic conditions leads to the formation of an enolate, which attacks the carbonyl carbon of another molecule to form a β-keto ester. Subsequent acid-catalyzed cyclization yields the chromenone ring system.
Not the question you are looking for? Ask here!
Enter question by text
Enter question by image
Unlock Smarter Learning with AskSia Super!
Join Super, our all-in-one AI solution that can greatly improve your learning efficiency.
30% higher accuracy than GPT-4o
Entire learning journey support
The most student-friendly features
Study Other Question