
Sia

Question
Chemistry
Posted almost 2 years ago
(i) Identify and provide a mechanism to account for its formation.
i).
ii).
3
A
(ii) Identify and provide a mechanism to account for its formation.
i).
ii).
4
iii).
B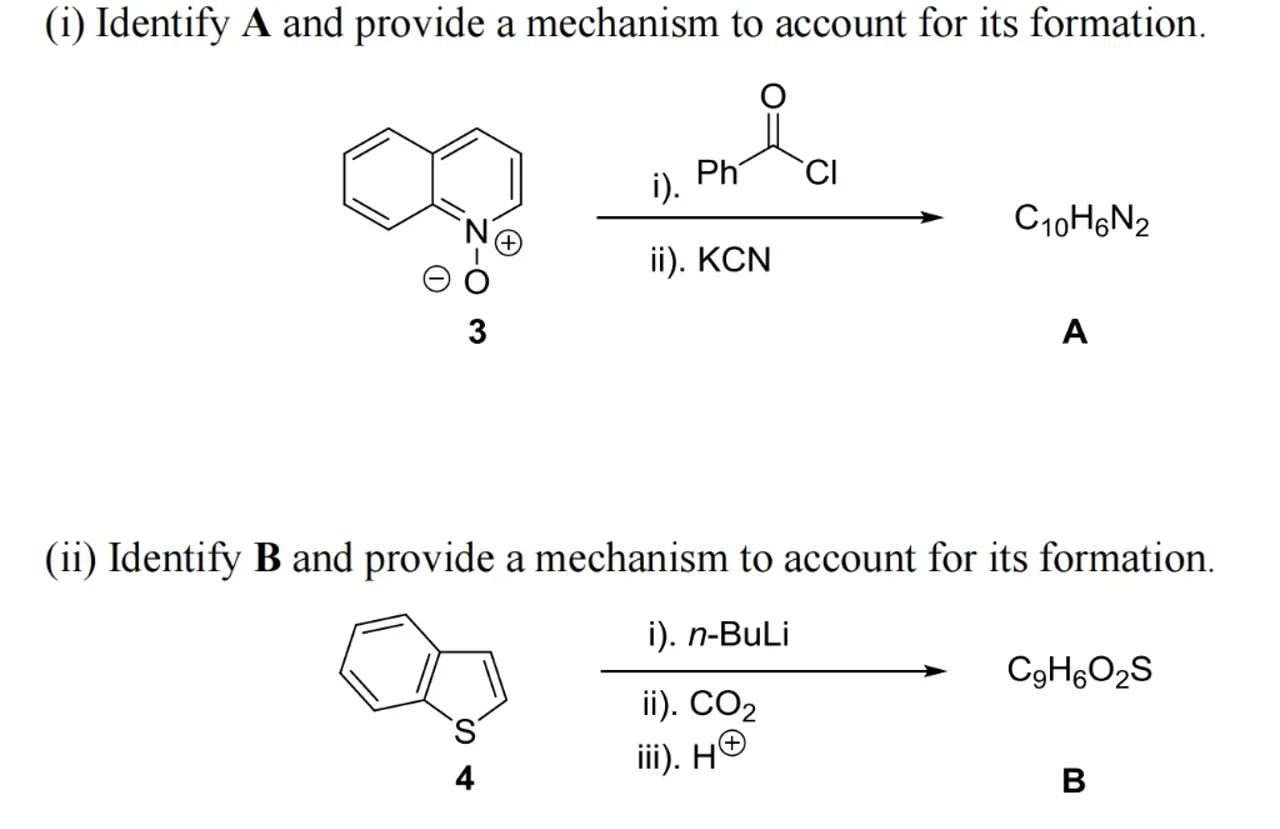

Answer from Sia
Posted almost 2 years ago
Solution
1
Identify Compound A: To identify compound A with the molecular formula , we need to consider the reagents used in its synthesis. The use of PhCOCl suggests acylation, and KCN indicates a nucleophilic substitution where a cyano group replaces a leaving group
2
Mechanism for the formation of A: The mechanism likely involves the formation of a ketone from the starting material 3 via Friedel-Crafts acylation followed by a nucleophilic substitution with KCN to introduce the cyano group
3
Identify Compound B: To identify compound B with the molecular formula , we need to consider the reagents used in its synthesis. The use of n-BuLi suggests deprotonation, CO2 indicates carboxylation, and H+ suggests an acid work-up, likely leading to the formation of a carboxylic acid
4
Mechanism for the formation of B: The mechanism likely involves the deprotonation of the starting material 4 by n-BuLi to form a carbanion, followed by carboxylation with CO2 to introduce a carboxyl group, and finally, protonation with H+ to yield the carboxylic acid
1 Answer
Compound A is likely a naphthalene derivative with a ketone and a cyano group. The mechanism involves Friedel-Crafts acylation followed by nucleophilic substitution with KCN.
2 Answer
Compound B is likely a thiophene derivative with a carboxylic acid group. The mechanism involves deprotonation by n-BuLi, carboxylation with CO2, and acid work-up with H+.
Key Concept
The identification of organic compounds and their mechanisms of formation is based on the molecular formula and the reagents used in the synthesis.
Explanation
Compound A is synthesized through acylation and nucleophilic substitution, while Compound B is synthesized through deprotonation, carboxylation, and protonation.
Not the question you are looking for? Ask here!
Enter question by text
Enter question by image
Unlock Smarter Learning with AskSia Super!
Join Super, our all-in-one AI solution that can greatly improve your learning efficiency.
30% higher accuracy than GPT-4o
Entire learning journey support
The most student-friendly features
Study Other Question